Silencing APOC3 expression with the investigational RNAi, plozasiran (ARO-APOC3), significantly reduced TG and TG-rich lipoproteins (TRLs) in patients with mixed dyslipidaemia in the Phase 2b MUIR trial (NCT04998201).
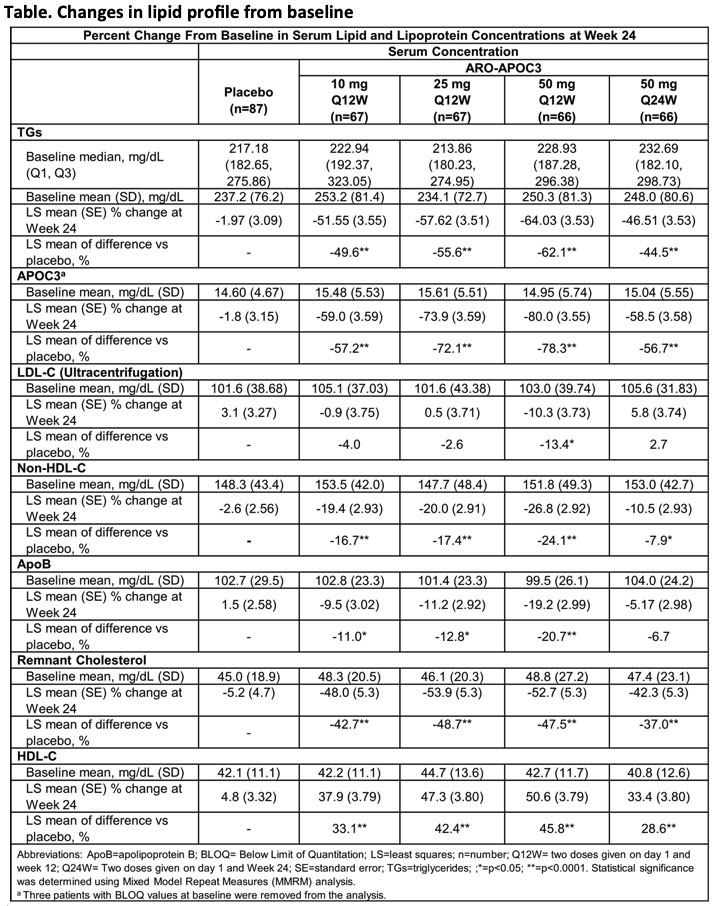
Week 24 data in the study of 353 patients with fasting TG 150-499 mg/dL and either LDL-C ≥70 mg/dL or non-HDL-C ≥100 mg/dL showed dose dependent reductions in least square (LS) mean APOC3 of up to -80% with plozasiran 10 mg, 25 mg or 50 mg s.c. administered on day 1 and at week 12, compared to placebo (p<0.0001) (Table).
LS mean TG was significantly reduced by up to -64% (p<0.0001), and LS mean non-HDL-C was reduced by up to -27%, apoB by up to -19%, and remnant cholesterol by up to -53%. LS mean HDL-C was increased by up to 51%. The most frequent adverse events were COVID-19 infection, worsening of glycaemic control, and upper respiratory infection.
The researchers concluded that plozasiran is a promising potential treatment for people at increased risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease due to elevated TRL, and that the MUIR data support further development of plozasiran in Phase 3 studies including a clinical outcomes trial.
Reference
Ballantyne CM. ARO-APOC3, an Investigational RNAi Therapeutic, Silences APOC3 and Reduces Atherosclerosis-Associated Lipoproteins in Patients With Mixed Dyslipidemia: MUIR Study Results. Presented at American Heart Association Scientific Sessions 2023 (11-13 November, Philadelphia, USA) PR.APS.P4 – Emerging Approaches to Lipid Lowering, Mo Mo3206




