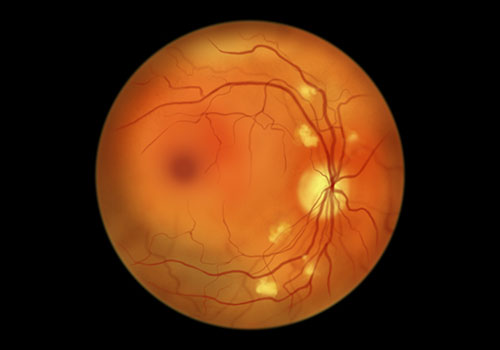
High triglyceride (TG) levels increase the risk of diabetic microvascular complications, according to results of a retrospective cross-sectional study including 1096 patients with type 2 diabetes (T2DM) and mean TG of 2.22 ±1.52 mmol/L.
Multivariate risk assessment showed that patients with T2DM and microvascular complications were at least twice as likely to have elevated TG levels as those without complications. High TG levels contributed to the risk of diabetic kidney disease (DKD), diabetic retinopathy (DR) and diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN), with odds ratios (ORs) of 2.447, 2.267, 2.252 respectively (95% confidence intervals: 1.648-3.633, 1.406-3.655, and 1.472-3.445). All increases were statistically significant (p<0.001).
In patients over 55 years, T2DM duration over 10 years, and HbA1c ≥ 7%, the risk of high TG was higher for DKD (ORs: 2.193, 2.419, 2.082), DR (ORs: 2.069, 2.317, 1.993), and DPN (ORs: 1.811, 1.405, 1.427).
The investigators pointed out that although previous studies have linked diabetic microvascular complications with high TG levels, the findings have been highly debated, and most previous studies analysed the association between lipid profiles and only one complication. As a result of their TG data, the investigators recommended that older patients with longer duration T2DM and higher HbA1c level should take particular care in controlling their lipid levels.
Reference
Li J, Shi L, Zhao G et al. High triglyceride levels increase the risk of diabetic microvascular complications: a cross-sectional study. Lipids Health Dis. 2023 Jul 31;22(1):109







